Civil 3D 2020 to 2022 Profile Essentials
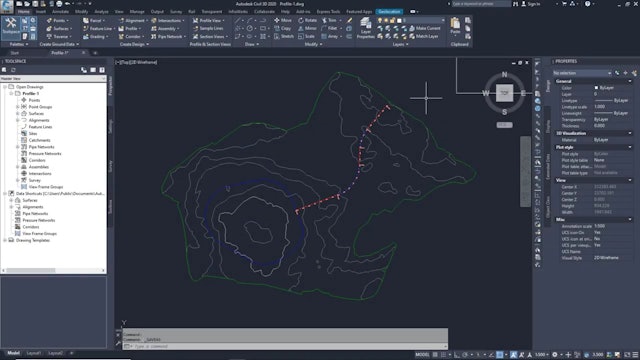
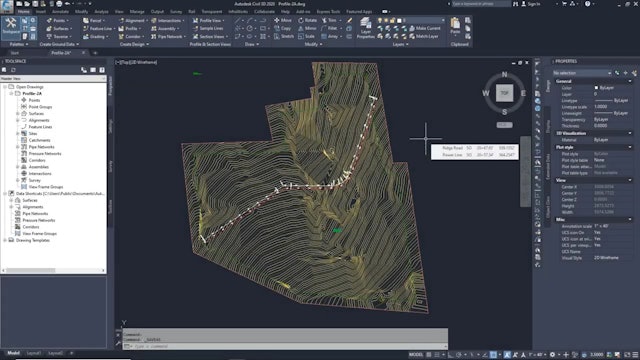
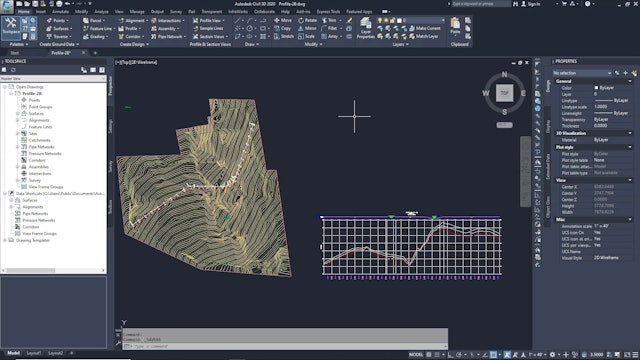
The main purpose of a profile is to show surface elevations along a horizontal alignment. Use profiles to visualize the terrain along a route of interest or across a particular region. There are several types of profiles: surface profiles, layout profiles, superimposed profiles, quick profiles, and corridor profiles.
Layout profiles use two types of curves: crest curves and sag curves. Crest curves are placed on hilltops or wherever the grade changes to a lesser value. There are three types of crest curves: a positive to negative grade transition, positive to positive, and negative to negative.
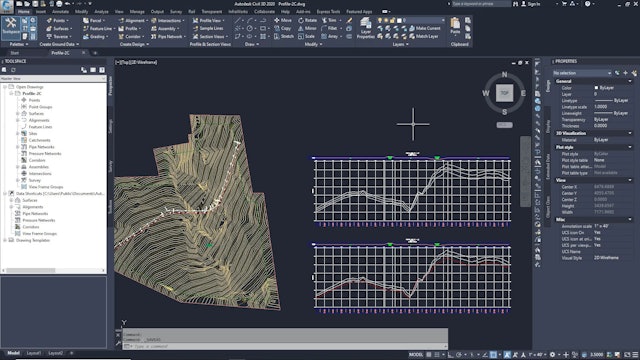
An offset profile is another type of profile commonly used in road design. While the road centerline provides the main horizontal alignment, various lines offset from the centerline mark other linear features, such as edges of pavement, ditches, and sidewalks. Profiles along these offsets can be analyzed in relation to each other and to the centerline profile for a more complete view of the surface along a corridor. Offset profiles are created and managed independently from any offset alignments that may exist, though both can be used together in the design process.
A profile view can contain projected objects such as points, feature lines, or AutoCAD blocks. These objects exist in plan view and are projected into a profile view so that you can visualize them in relation to a profile.
-
01 Designing Simple Profiles in Civil 3D
-
02 Creating and Displaying Surface Profiles with Offsets in Civil 3D
-
03 Changing the Profile Style
-
04 Reviewing Surface Profile Characteristics
-
05 Creating a Layout Profile
-
06 Editing a Layout Profile
-
07 Copying a Profile and Offsetting it Vertically